Test Management¶
Attention
This module is part of Tuleap Entreprise. It might not be available on your installation of Tuleap.
The Test Management plugin of Tuleap aims at providing a simple and easy way to deal with test campaigns.
Test Management features:
- Create and maintain test case definitions
- Create test campaigns as a collection of test cases
- Follow test executions (Not run, passed, failed, blocked)
- Realtime update for concurrent test execution by team
Overview¶
Here are the main concepts with Tuleap Test Management:
- Test Case: it’s the description of something to test. The definition is meant to be re-used
- Test Campaign: a collection of Test Case to run.
- Test Execution: it’s the execution of one Test Case in the context of a Test Campaign
- Environment: a given Test Excecution can run in different contexts (Same test but different setup)
Test Case, Test Campaign and Test Execution are 3 different trackers. Environment is a property of “Test execution”.
Note
Test Management is stable and used since 1.5 year at Enalean for all Tuleap releases without any issues.
Run a Test Campaign¶
The welcome screen of Test Management lists all active Test Campaigns with a quick overview of the overall progress and the ability to access the test list.
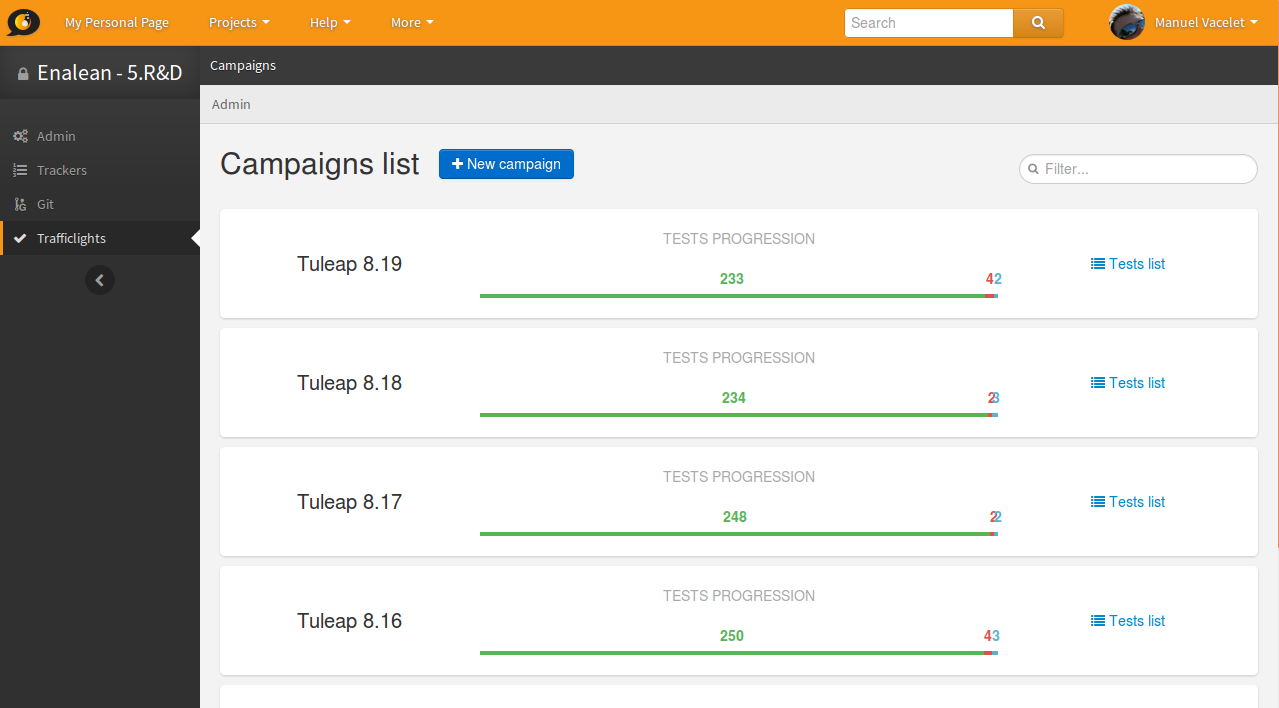
By hitting “Test list” you will see the list of tests proposed in the given campaign.
In the following figure, the user selected a test that “Passed”.
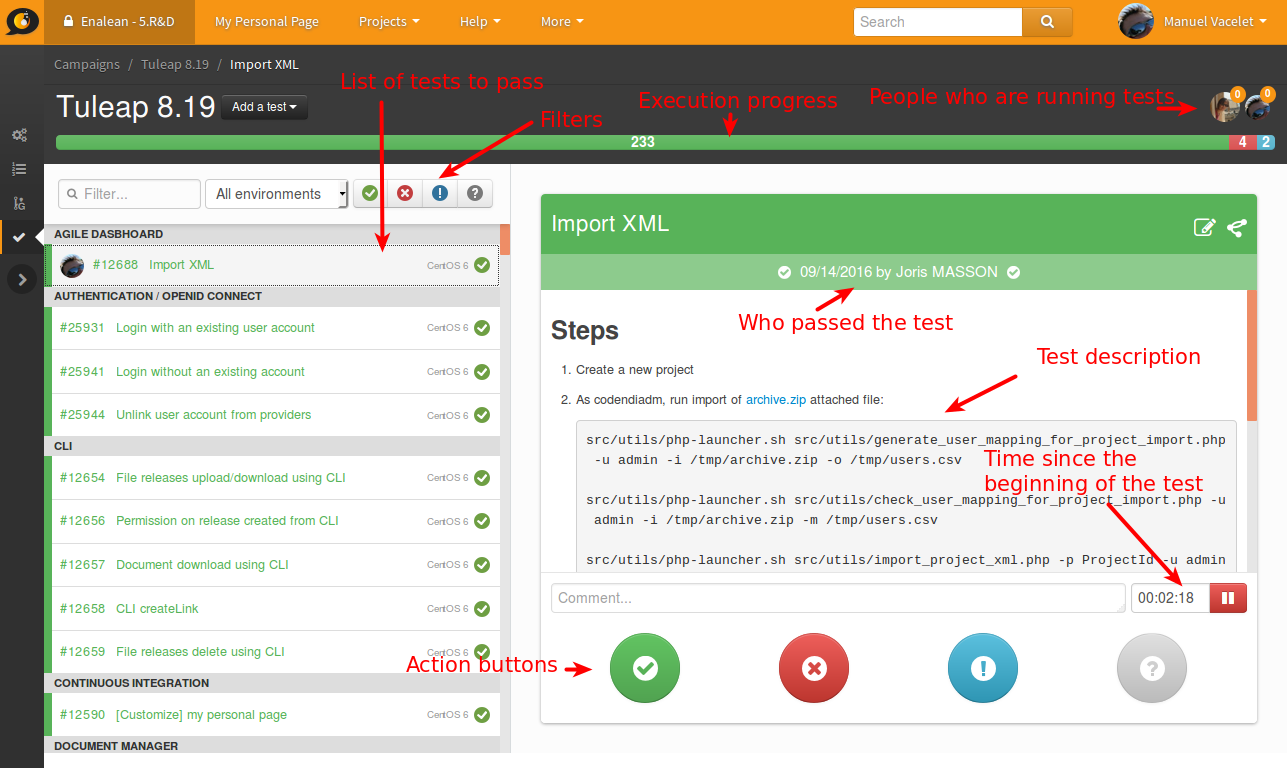
Tests can have following status:
- Not run, this is the default
- Passed, the test was successful
- Failed, the test lead to an error
- Blocked, the test cannot be run
One can switch from one state to another (a test can be “Not run” then “Passed”, re-switched to “Not run” because tester didn’t get what was described to finish by “Faild”).
Tuleap will record the time taken for each test. It works this way:
- It starts as soon as you load the test definition.
- It ends when you hit one of the action buttons.
Time is not yet used in the interface, it’s only recorded for a future usage. You can see the value and make your own computation from the “Test Execution” tracker.
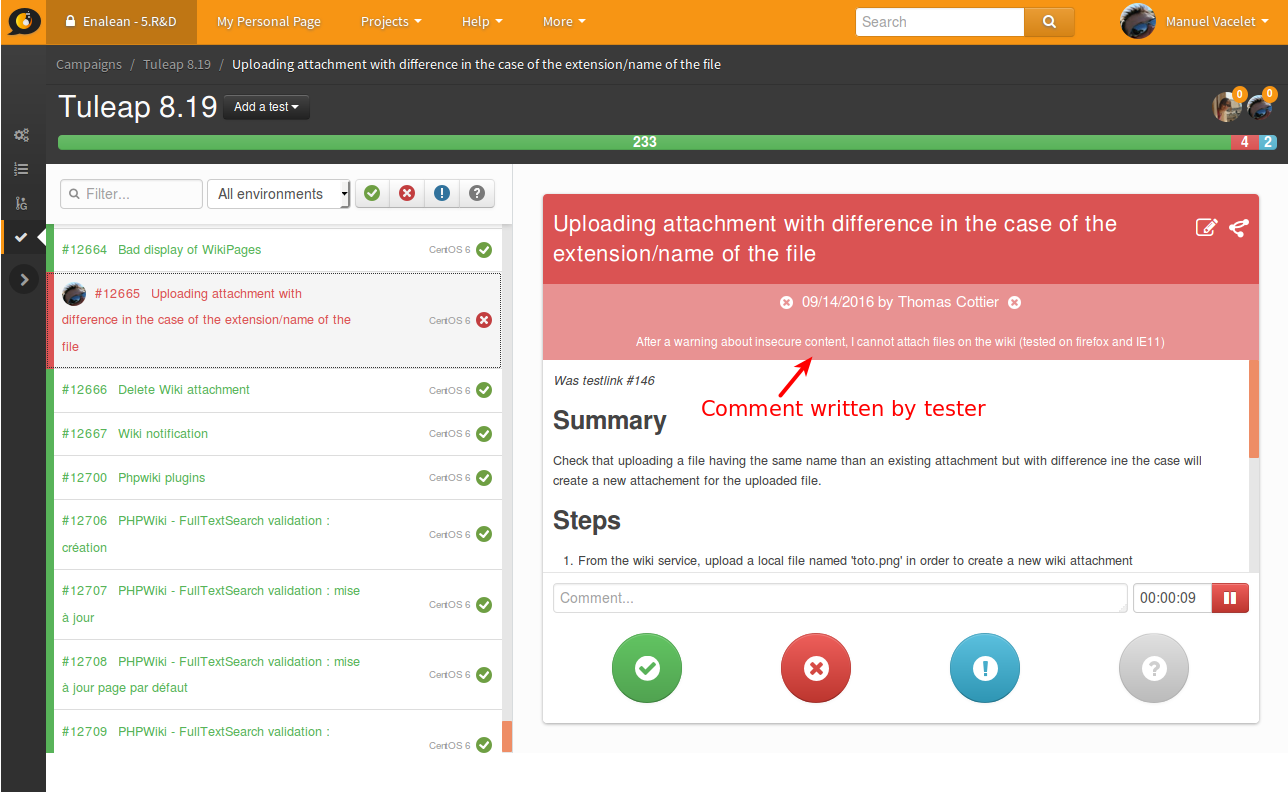
Example of test failure:
Modify or create tests¶
You can create tests directly inside the “Test Case” tracker, it means that you benefit of all tracker power for artifact creation:
- Create one after another
- Import from CSV
- Import via REST
- Import via XML
You can also directly create tests in campaigns, this is convenient if you don’t already have a base of tests or if you want to create test.
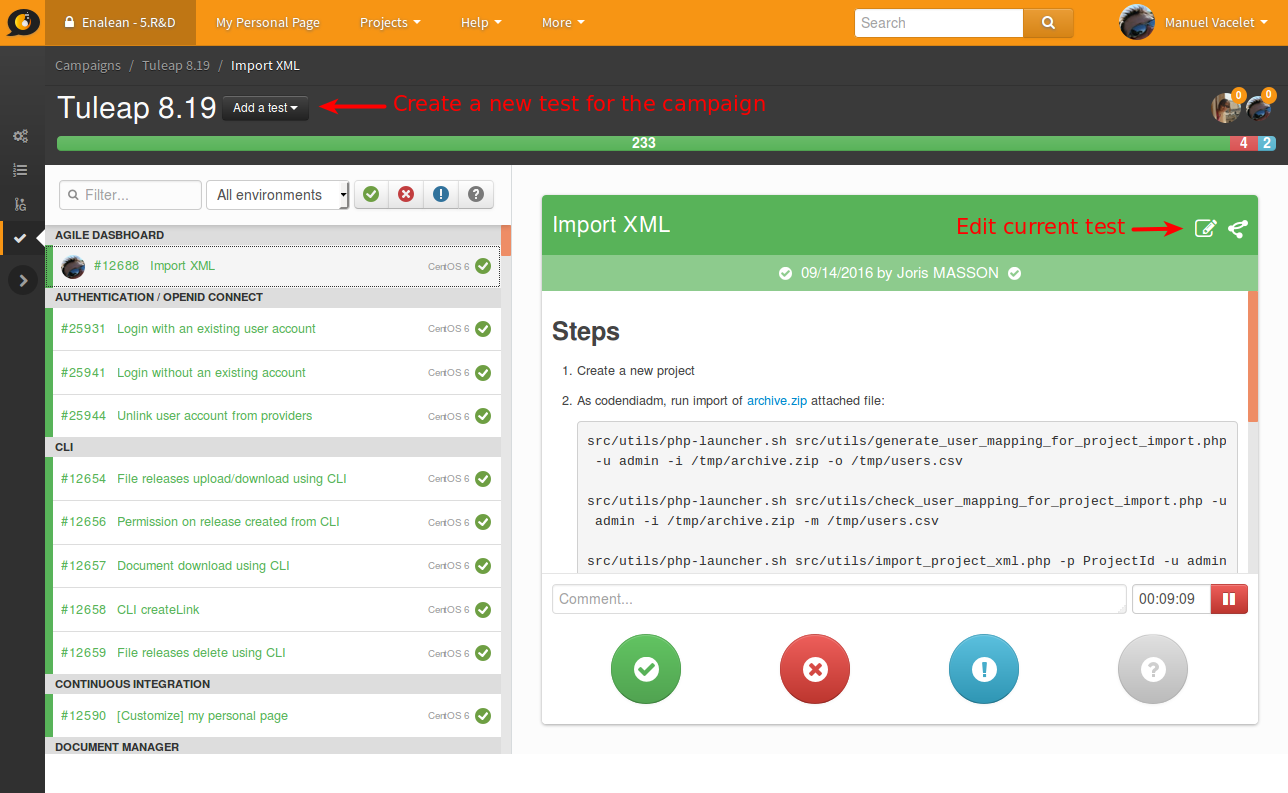
You can also edit the test directly from the interface.
The test you create or you edit are automatically updated in the test campaign and will be re-usable in a following campaign.
Test steps¶
Starting Tuleap 10.3, a test case can be divided into steps. Each step have to be run in the campaign.
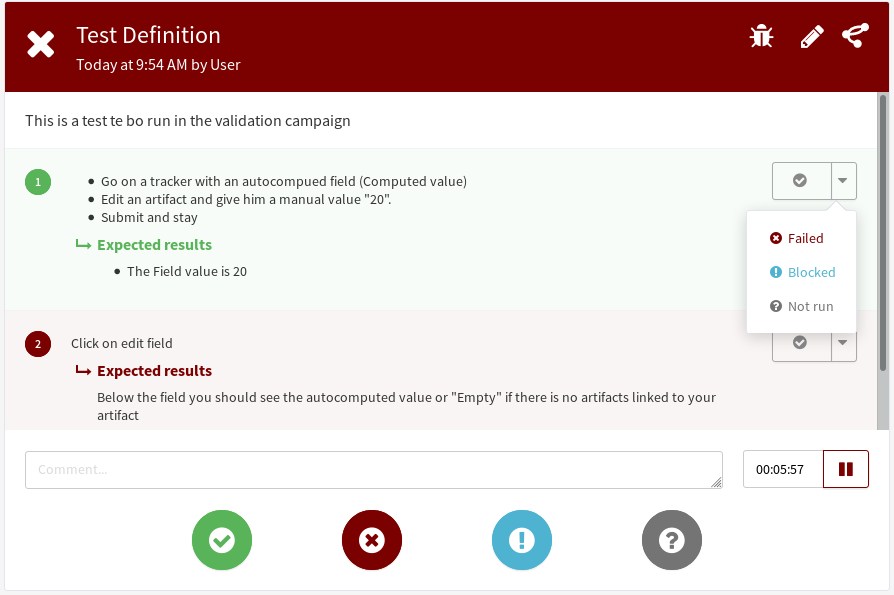
These steps provide a global result for the tests:
- All steps are done -> test done
- At least one step failed -> test fail
- At least one step is blocked -> test blocked
- At lest one step is not run -> test not run
Create or modify steps for your tests¶
There are two new fields to add in your testmanagement trackers to be able to defined your steps:
- Field
step definitioninto Test definition tracker - Field
step executioninto Test execution tracker.
If one of this field is missing, steps cannot be run. In addition, these fields can only be added in the Test definition tracker and Test exec tracker defined in your testmanagement configuration.
To have working steps, these 2 fields must have a specific shortname:
- Field
step definitionmust have the shortnamesteps - Field
step executionmust have the shortnamesteps_results
Once these fields added, you can defined your step in your test case by editing the artifact:
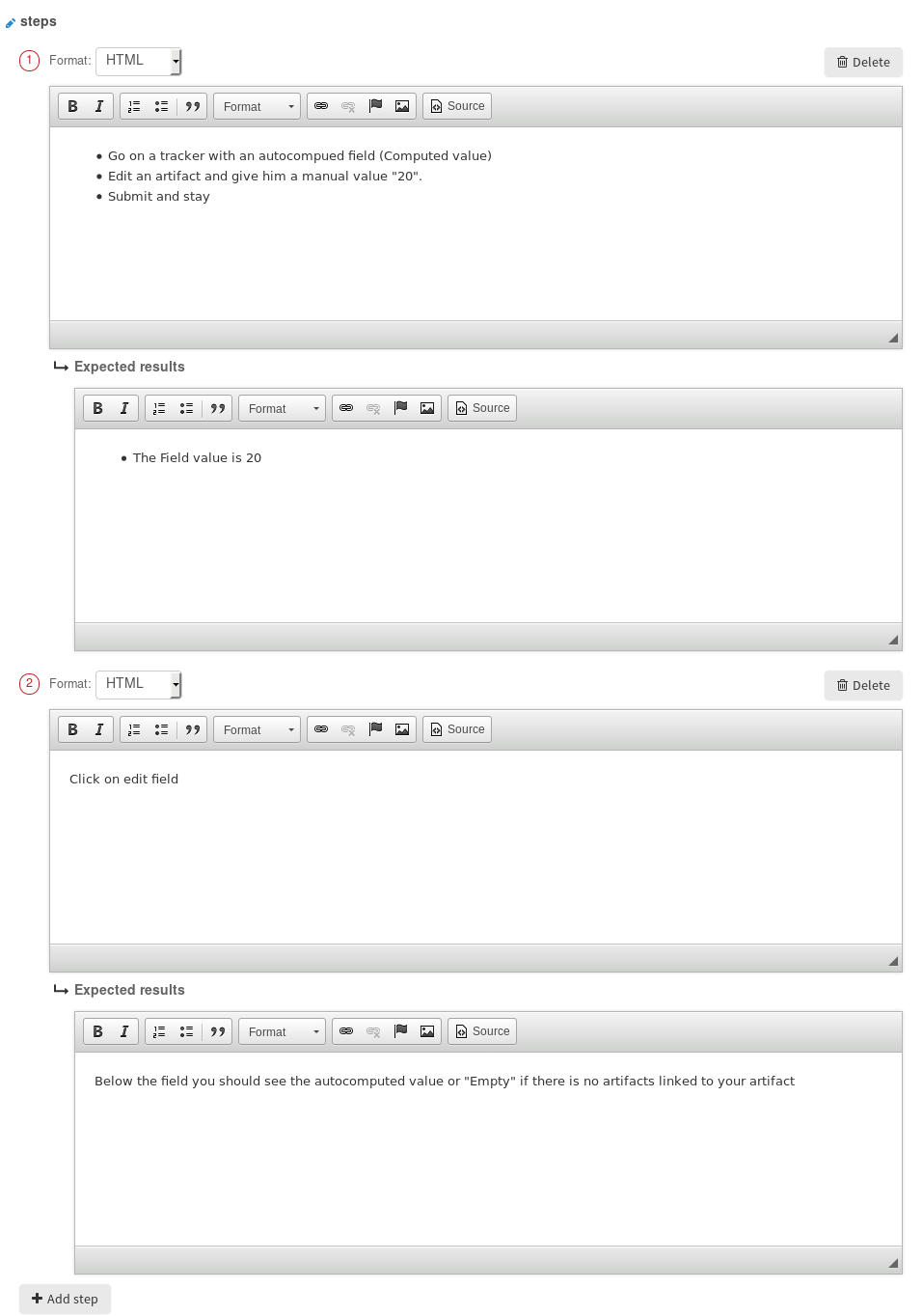
Create a Test Campaign¶
From the home page of the service, there is “New campaign” button that will open the Campaign creation screen.
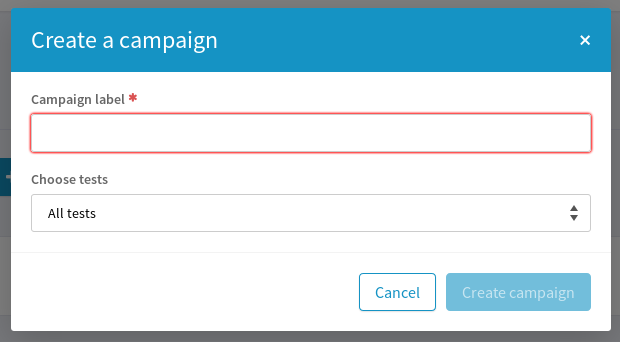
You need to give a name to your campaign and select which tests you want to execute during your validation campaign.
Adding Tests to a Campaign¶
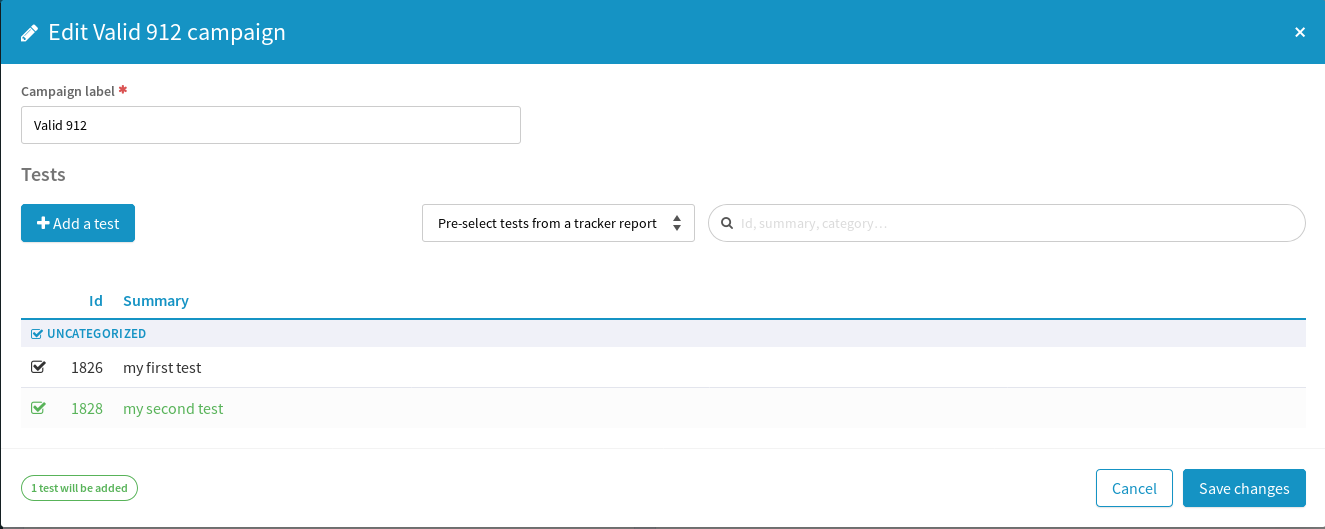
Once the validation has started you might want add some new tests to your campaign. Open your campaign by clicking on “Details button”.
Then click on the “Edit” button.
A new modal will enable you to look for existing artifacts or to create directly a new one.
Link with Agile Dashboard¶
If your project also uses the Agile Dashboard service, a “Test campaigns” tab will be added to milestones.
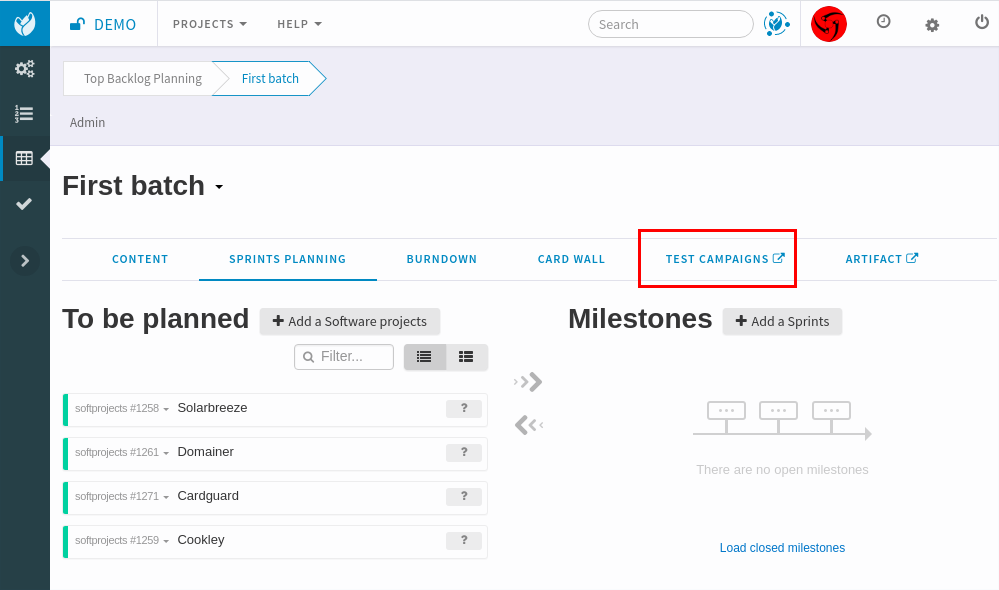
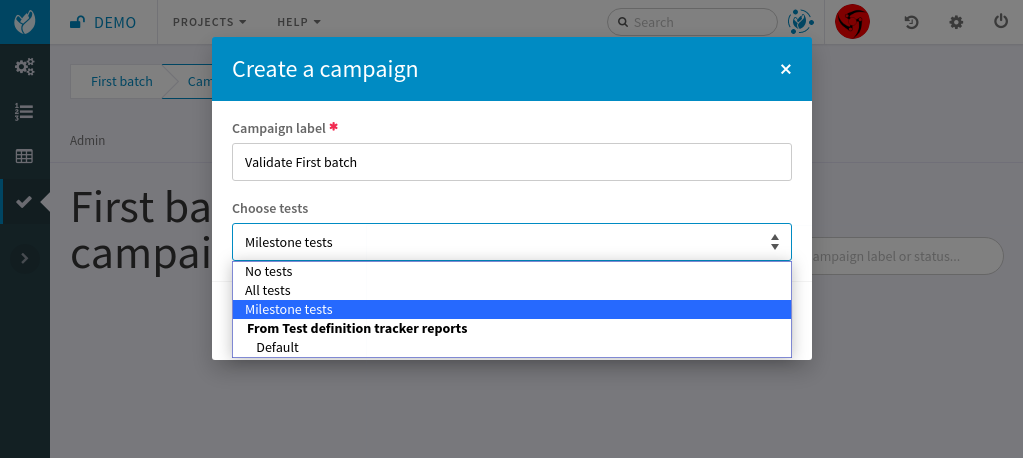
After clicking on this tab, you will be able to create a new test campaign from Test definitions linked to the Milestone’s items. For example, you have a user story in a Release “Version 1.0”. You can link a Test definition to this user story.
Navigate to the “Version 1.0 milestone, click on the “Test campaigns” tab and then create a new campaign. In the modal, you can choose “Milestone tests” which will select all the test definitions linked to “Version 1.0” milestone’s user stories.
Test automation¶
Note
This section is experimental and you will need to have access to ttm CLI tool to make it works. Ask your Enalean
representative if you want to go further.
TTM is able to consolidate automated test results inside its campaign. This way you can have a mixed campaign with both manual and automated tests. The key principles are:
- TTM relies on an external tool like Jenkins to execute tests. Any CI tool can be used.
- Test automation itself is not TTM business, you can use whatever tool you want (robot framework, cypress, selenium, etc) as long as it produces a junit XML output with results.
- Automated tests are stored in a SCM (git or subversion)
- The link between TTM and test results is done by associating TTM Test Definitions and Junit Test Suite
- One Test Definition can be linked to one Test Suite at max
- One Test Suite can be linked to one Test Definition at max
In the next sections we will describe how to setup TTM with Jenkins.
This assumes a couple of things:
- The server where Tuleap is installed is located at
https://tuleap.example.com - The project where TTM is enabled is called ‘test-automation-demo’ (its shortname)
Users and credentials¶
First you need to create a new Tuleap user that will be used by Jenkins to report test results. This user must be configured Tuleap side with the appropriate permissions to update “Test Executions” and read “Test Definitions”. We recommend using a dedicated user with limited permissions to reduce risks of credentials leaking.
At Jenkins side, you need to register this Tuleap user in the “Credentials” section. Create a new entry for “username and
password” and give it a descriptive id like jenkins-tuleap-bot.
You also need to upload the ttm binary on Jenkins server.
Configure TTM¶
The “Test Definitions” tracker must have one string or text field with name automated_tests. We recommend to add it
close to “Description”. You can set whatever label you want, only the name is meaningful.
Note
Starting from Tuleap 9.19 the automated_tests field is part of the default Test Management tracker templates.
Jenkinsfile scaffolding¶
In your local working copy of your automated tests we assume that you are able to run them locally and get a junit XML result. The following commands will create two files in your repository to allow test execution and reporting:
Jenkinsfilefor jenkins job configuration.ttm.ymlfor TTM configuration
Execute it like
$> ttm scaffold --use-campaign-name \
--credentials-id jenkins-tuleap-bot \
--server https://tuleap.example.com \
--project-name test-automation-demo \
--junit-file tests_results.xml
In the previous command:
--credentials-idrefers to the ID of the username + password credential you configured in the previous section--servercorresponds to the Tuleap server URL where TTM is running--project-namecorresponds to the Tuleap project’s shortname, where your campaign is--junit-filelocates where the automated test results are generated within you working copy
Then you should edit the generated Jenkinsfile to adjust Build and Test phases to your process. You can create as many
steps and stages as needed, the only constraint is to keep the def ttm_credentials and the stage('Reporting').
Once you’re done, add Jenkinsfile and .ttm.yml files, commit and push.
Associate automated tests results and test definitions¶
You need to associate testsuite from your junit test results and Test Definitions artifacts. ttm cli tool has
a helper to assist you with that: ttm verify.
$> ttm verify --username jenkinsbot
Enter Password: xxxxx
Test suites with a match in TTM
Test suites without a test definition
'AccountingBalanceTest' with 5 test cases
'LoginWithUsernameTest' with 12 test cases
'SendInvoiceTest' with 1 test cases
At first run it indicates that no test suites have been linked to a test definition.
You need to go in your test definitions artifacts and set in “automated_tests” field the test suite name (eg. ‘AccountingBalanceTest’).
Once done, you can run again the verify command:
$> ttm verify --username jenkinsbot
Enter Password: xxxxx
Test suites with a match in TTM
'AccountingBalanceTest' (test #2446)
'LoginWithUsernameTest' (test #2512)
Test suites without a test definition
'SendInvoiceTest' with 1 test cases
At this point you’ve got everything you need to report test results. You can test it by yourself by creating a new test
campaign “Test automated ttm” with the selected test definitions and run the send-results by hand:
$> make tests
$> ttm send-results --username jenkinsbot --campaign-name "Test automated ttm"
Then check the status of your campaign in Test Management.
Configure Jenkins job¶
Create a new Jenkins job “Pipeline” and point it to your SCM repository (you might want to use jenkins-tuleap-bot
credentials to access the repo). You should also allow it to be triggered remotely. Check the “Trigger builds remotely” checkbox in the “Build Triggers” section and provide a secret Authentication token.
Run a first build to configure the job. This job will fail.
At second run it should prompt for a campaign name. Create a new campaign “Test automated ttm from jenkins” with the same test definitions than in previous steps. After a few moment, the pipeline should succeed and your test campaign in Test Management is updated.
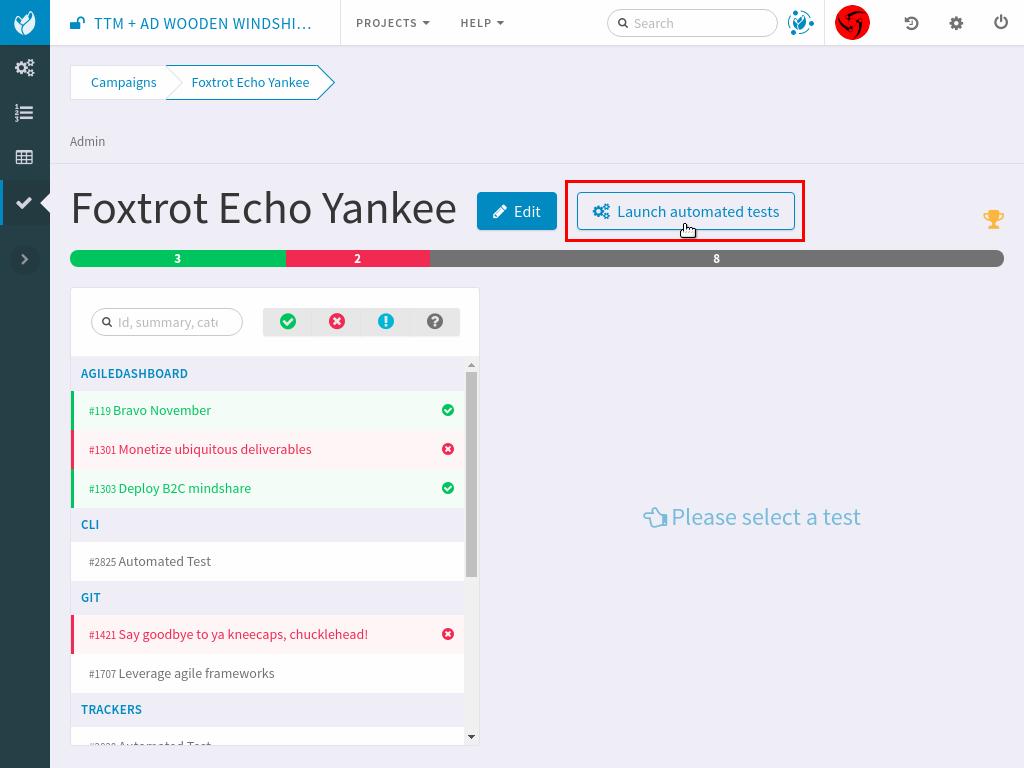
Launch automated tests from the Test Management campaign¶
Edit your Campaign in Test Management and fill in the Jenkins job URL for the job you have just configured. Also fill in the Authentication token defined in the step before.
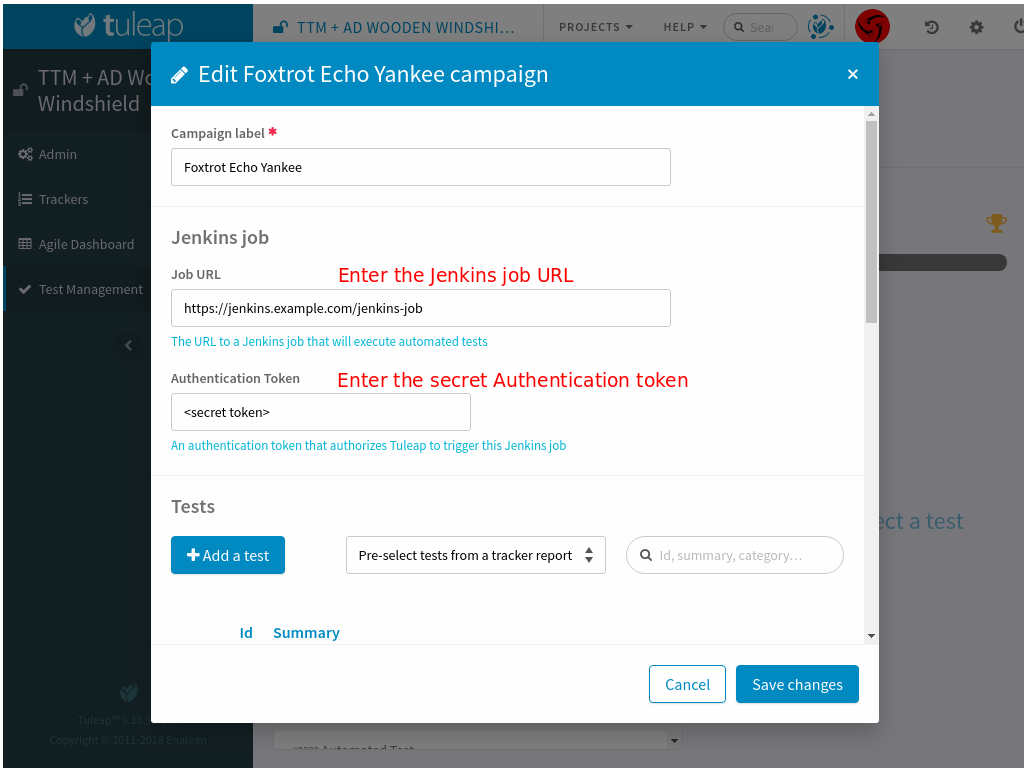
Once the campaign is configured, a button will appear in the Campaign details next to the Edit button: “Launch automated tests” The button lets you trigger the Jenkins job which will run the automated tests and set the corresponding Test executions to “Passed”!